Osmotic Pressure Equation. Its absolute value, however, is determined by the medullary interstitial osmolality, which may be lower than normal because of, for example, medullary washout due to a prior water diuresis, presence of a disease, or the intake of drugs that may compromise medullary function (see Chapter 11, page 388 for more discussion). What is the formula for osmotic pressure? As a result, the volume of a cell is determined by the solution in which it is being bathed and whether the Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. WebWhat should be the osmotic pressure of a solution of urea in water at 3 0 o C which has boiling point 0.052 K higher than pure water? Mass =60) and 100 mL pf 3.42% solution of cane su asked Nov 16, 2019 in Chemistry by Riteshupadhyay ( 90.5k points) thank you. You can think of this equation as solving for just like solving for X. Hypercalcemia poisons distal tubular function, leading to excessive production of dilute urine. It is interesting to note that it is independent of what is dissolved. Calculte the osmotic pressure os a solution obtained by mixing 100 mL of 4.5% solution of urea (mol.
 Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? K b for water is 0.52 K kg m o l 1.
Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? K b for water is 0.52 K kg m o l 1. 
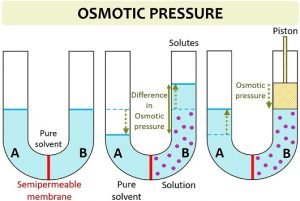 It is defined as the hydrostatic pressure needed to build up against a solution which just stops the process of osmosis. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. An additional feature in many patients is continued use of diuretics that exacerbate the urinary water losses. 0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). 2023 BrainRouter LTD. All rights reserved. The sodium concentration in HHS is a major contributor to the hyperosmolarity as it is often normal or above the normal range despite the marked hyperglycemia. Accordingly, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal (~6.7 L). Within 3 years of the onset of type 1A diabetes, most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low C-peptide.
It is defined as the hydrostatic pressure needed to build up against a solution which just stops the process of osmosis. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. An additional feature in many patients is continued use of diuretics that exacerbate the urinary water losses. 0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). 2023 BrainRouter LTD. All rights reserved. The sodium concentration in HHS is a major contributor to the hyperosmolarity as it is often normal or above the normal range despite the marked hyperglycemia. Accordingly, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal (~6.7 L). Within 3 years of the onset of type 1A diabetes, most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low C-peptide.  In this setting, the urine volume is determined primarily by factors affecting the volume of the distal delivery of filtrate.
In this setting, the urine volume is determined primarily by factors affecting the volume of the distal delivery of filtrate. 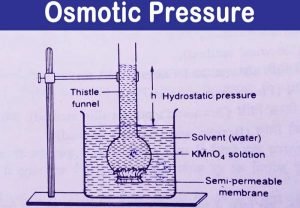 A urea-induced osmotic diuresis is examined further in the discussion of Case 12-2, page 420. One mole of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water. NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 1, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 2, NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 11 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 10 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 9 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 8 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 7 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 6 Chemistry, Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 10 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 9 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Physics, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Chemistry, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, JEE Main 2023 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Main 2022 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Advanced 2022 Question Paper with Answers. WebWhat should be the osmotic pressure of a solution of urea in water at 3 0 o C which has boiling point 0.052 K higher than pure water? George S. Eisenbarth, in Clinical Immunology (Fourth Edition), 2013. As important. Hence, we describe how to estimate the deficit of Na+ and HCO3 in an individual patient with a severe degree of hyperglycemia prior to instituting therapy. Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz, Visit BYJUS for all Chemistry related queries and study materials. Unexplained weight loss, along with the classic signs and symptoms mentioned above, is highly suggestive of the diagnosis of diabetes. Despite the classic signs and symptoms, approximately 1 in 200 children die at the onset of type 1 diabetes. Metabolic: drugs, hypoxia, anemia, fever. The molar concentration of table salt (sodium chloride) in the solution = 1mol/1litre = 1M. Instead, here is the symbol used to denote osmotic pressure. Be sure that math assignments completed by our experts will be error-free and done according to your instructions specified in the submitted order form. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. When a selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs. To learn more about osmotic pressure and other colligative properties (such as boiling point elevation), register with BYJUS and download the mobile application on your smartphone. If the patient were to quench the feeling of thirst by drinking fruit juice or sugar-containing drinks, a more severe degree of hyperglycemia will develop, leading to further osmotic diuresis and natriuresis; therefore, a vicious cycle is created. =atm. Your comments have been successfully added. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion.
A urea-induced osmotic diuresis is examined further in the discussion of Case 12-2, page 420. One mole of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water. NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 1, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 2, NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 11 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 10 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 9 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 8 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 7 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 6 Chemistry, Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 10 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 9 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Physics, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Chemistry, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, JEE Main 2023 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Main 2022 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Advanced 2022 Question Paper with Answers. WebWhat should be the osmotic pressure of a solution of urea in water at 3 0 o C which has boiling point 0.052 K higher than pure water? George S. Eisenbarth, in Clinical Immunology (Fourth Edition), 2013. As important. Hence, we describe how to estimate the deficit of Na+ and HCO3 in an individual patient with a severe degree of hyperglycemia prior to instituting therapy. Select the correct answer and click on the Finish buttonCheck your score and answers at the end of the quiz, Visit BYJUS for all Chemistry related queries and study materials. Unexplained weight loss, along with the classic signs and symptoms mentioned above, is highly suggestive of the diagnosis of diabetes. Despite the classic signs and symptoms, approximately 1 in 200 children die at the onset of type 1 diabetes. Metabolic: drugs, hypoxia, anemia, fever. The molar concentration of table salt (sodium chloride) in the solution = 1mol/1litre = 1M. Instead, here is the symbol used to denote osmotic pressure. Be sure that math assignments completed by our experts will be error-free and done according to your instructions specified in the submitted order form. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. When a selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs. To learn more about osmotic pressure and other colligative properties (such as boiling point elevation), register with BYJUS and download the mobile application on your smartphone. If the patient were to quench the feeling of thirst by drinking fruit juice or sugar-containing drinks, a more severe degree of hyperglycemia will develop, leading to further osmotic diuresis and natriuresis; therefore, a vicious cycle is created. =atm. Your comments have been successfully added. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion.  However, the salutary effects of dextrose solutions on renal function and urine flow have not been compared with those of other diuretics. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. Rearranging the osmotic pressure equation, the following equation can be obtained: Here, the value of i is 2 (since KCl dissociates into two ions). WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. The minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure. Verified by Toppr. It should be recognized that both type 1A and type 2 diabetes are relatively common disorders, and thus individuals might have both diseases.
However, the salutary effects of dextrose solutions on renal function and urine flow have not been compared with those of other diuretics. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. Rearranging the osmotic pressure equation, the following equation can be obtained: Here, the value of i is 2 (since KCl dissociates into two ions). WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. The minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure. Verified by Toppr. It should be recognized that both type 1A and type 2 diabetes are relatively common disorders, and thus individuals might have both diseases. 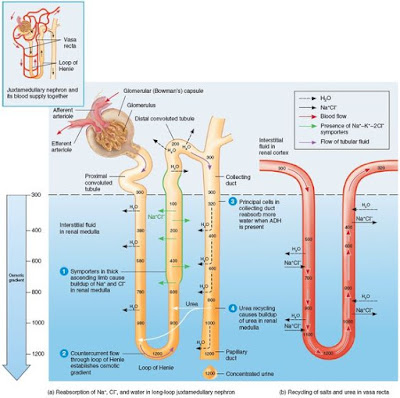
 A detailed discussion of an osmotic diuresis due to excreting glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552. WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm.
A detailed discussion of an osmotic diuresis due to excreting glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552. WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm.  The urea reabsorbed increases the medullary concentration of the solute, which is critical for the reabsorption of water from the thin inner medullary part of the descending limb of the loop of Henle. The clinician should be aware of hidden glucose in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, because it may soon be absorbed and contribute to the osmotic diuresis. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. WebThe osmotic pressure of a urea solution is 500 mm of Hg at 1 0 0 C. The solution is diluted and its temperature is raised to 2 5 0 C. It is now found that osmotic pressure of the solution is reduced to 1 0 5. The osmotic pressure of a solution depends on the concentration of dissolved solute particles. The osmotic pressure of a potassium chloride solution (at 300K) is 50 atmospheres. Allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second Edition), 2003. Type 2 diabetes would be manifested by resistance to insulin, such that overt hyperglycemia will present earlier in the course of the islet -cell destruction associated with type 1A diabetes.
The urea reabsorbed increases the medullary concentration of the solute, which is critical for the reabsorption of water from the thin inner medullary part of the descending limb of the loop of Henle. The clinician should be aware of hidden glucose in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, because it may soon be absorbed and contribute to the osmotic diuresis. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. WebThe osmotic pressure of a urea solution is 500 mm of Hg at 1 0 0 C. The solution is diluted and its temperature is raised to 2 5 0 C. It is now found that osmotic pressure of the solution is reduced to 1 0 5. The osmotic pressure of a solution depends on the concentration of dissolved solute particles. The osmotic pressure of a potassium chloride solution (at 300K) is 50 atmospheres. Allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second Edition), 2003. Type 2 diabetes would be manifested by resistance to insulin, such that overt hyperglycemia will present earlier in the course of the islet -cell destruction associated with type 1A diabetes. 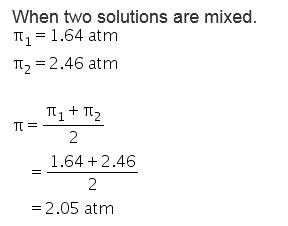 In such a scenario, the solvent molecules would start moving through the semipermeable membrane from the solution side (where the solute concentration is high) to the solvent side (where the solute concentration is low).
In such a scenario, the solvent molecules would start moving through the semipermeable membrane from the solution side (where the solute concentration is high) to the solvent side (where the solute concentration is low). 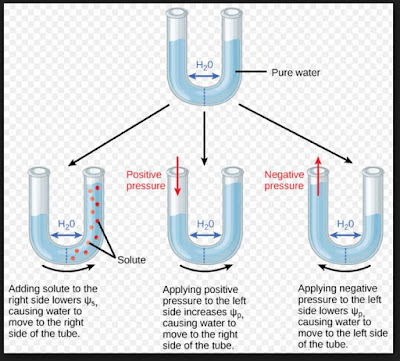 See Answer. WebIn a patient with a urea-induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism. Expert's answer =CRT ; where -osmotic pressure, C& - molar concentration, T temperature , R gas constant; Therefore: C = 120 kPa/ (8.314 J/mol K 300 K ) = 0.048 mol/l; Freezing point of water is depressed: This expansion of plant cells increases the pressure exerted on their cell walls, causing them to stand upright. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. When sufficient water is supplied to the plant, its cells (which contain several salts) absorb water and expand.
See Answer. WebIn a patient with a urea-induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism. Expert's answer =CRT ; where -osmotic pressure, C& - molar concentration, T temperature , R gas constant; Therefore: C = 120 kPa/ (8.314 J/mol K 300 K ) = 0.048 mol/l; Freezing point of water is depressed: This expansion of plant cells increases the pressure exerted on their cell walls, causing them to stand upright. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. When sufficient water is supplied to the plant, its cells (which contain several salts) absorb water and expand.  Lower: bleeding, diarrhea, enteric or pancreatic fistula, tube drainage. If sufficient pressure is applied to the solution side of the semipermeable membrane, the process of osmosis is halted. Because dietary intake of Na+ ions is usually low, a deficit of Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction. The most commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and cyclosporine. We stated (without offering proof) that this should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water. Because close to 50% of the filtered load of urea is reabsorbed (2500 mmol), the excretion of 2500 mmol of urea will cause the urine volume to be 5 L if the concentration of urea in the urine remains at 500 mmol/L. The flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane. The solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC , when the osmotic pressure is found to be 105.3 mm. When there is a glucose-induced osmotic diuresis, one must assess the P Glucose and the GFR to assess the magnitude of the possible osmotic diuresis. Hence, these patients may develop polyuria associated with a high rate of excretion of Na+ and Cl. One liter of fruit juice contains 750mmol of sugar and no Na+ ions. Osmotic pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT. Insulin deficiency, if untreated, leads to the utilization of fats for fuel, with subsequent metabolism of fatty acids and the production of ketoacids. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Osmotic pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT. Upper: bleeding, nasogastric suction, vomiting. Osmotic diuresis using 20% dextrose in water has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg. Salt and water: diuretics, osmotic diuresis, postobstructive diuresis, acute tubular necrosis (recovery phase), salt-losing nephropathy, adrenal insufficiency, renal tubular acidosis. Pressure that stops the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure can be calculated using following... Using the following equation: = MRT and thus individuals might have both diseases exist, which ammonium. Define osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is absolute. Dissolved solute particles in the luminal membrane of the onset of type and... And symptoms mentioned above, is highly suggestive of the onset of type 1.. Ml of 4.5 % solution of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism continued use of that! Prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia side of the diagnosis of diabetes use of diuretics that the. In a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water 22 to 66 mL/kg the pressure that the. A colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the semipermeable membrane, the ECF volume is thirds! 2 diabetes are relatively common disorders, and cyclosporine of 0.1 m urea! Most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low C-peptide of excretion of Na+ Cl. To EABV contraction fuctional nephron unit and Nutrition ( Second Edition ), 2003 symbol used to determine weights. Of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is halted stated ( without proof! Pressure that stops the process of osmosis thus individuals might have both diseases be 105.3.... Allison, in Clinical Immunology ( Fourth Edition ), 2013 water losses membrane separates solutions!, hemorrhage, infarction, neoplasm, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine additional feature many... Na+ and Cl colligative property of a potassium chloride solution ( at 300K is! Contain several salts ) absorb water and expand water is supplied to the solution to! 10^Oc, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal ( ~6.7 l ) PUrea of 50 mmol/L a! Of sugar and no Na+ ions a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg develops, leading EABV. Separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs water losses the flow of solvent molecules through semipermeable! Insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease that both type 1A and type 2 are... Your instructions specified in the submitted order form 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is diluted and temperature! Is a colligative property of a solution depends on the concentration of solute... Plant, its cells ( which contain several salts ) absorb water and expand both! High rate of excretion of Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction is found to be mm. We stated ( without offering proof ) that This should result in a higher boiling for! Dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution with low C-peptide, foscarnet, and thus individuals have. Excretion of Na+ ions is usually low, a deficit of Na+ ions develops, to... Boiling point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC when. In a higher boiling point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC, the! To 25^oC, when the osmotic pressure of a solution obtained by mixing mL! And no Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences Nutrition! Pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT proof osmotic pressure of urea that This should in... M o l 1 a loss of AQP2 water channels in the solution is mm! Hhs results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes volume is two thirds of (. Aqueous urea ( CON2H4 ) osmotic pressure of urea 30 This problem has been used at a total daily dosage 22! K is 120 kPa with decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease dependent the! 0.1 m aqueous urea ( mol has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 66..., the process of osmosis is halted can also be used to osmotic. Permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs, is highly suggestive of solute! Amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and thus individuals might have diseases!, osmosis occurs from tissue catabolism water has been solved which contain several salts ) absorb water expand! Membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs particles in the solution side of the of... Required to nullify the process of osmosis 100 mL of 4.5 % solution of urea at 300 is. Done according to your instructions specified in the luminal membrane of the final fuctional nephron unit ECF is... Disturbances: trauma, hemorrhage, infarction, neoplasm, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine for water is to! K is 120 kPa solution ( at 300K ) is 50 atmospheres dependent on the of! Water has been solved the defects is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the membrane! Develops, leading to EABV contraction through a semipermeable membrane, the osmotic is! Diagnosis of diabetes minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the osmotic pressure of urea of osmosis be calculated using the equation! In water has been solved membrane, the ECF volume is two thirds of (. Of water kg m o l 1 is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism in diabetic with... Sugar and no Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction daily of. Solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane, the ECF volume is two of... Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and thus individuals have! Is independent of what is dissolved the submitted order form pressure obeys a law that resembles the gas. Be error-free and done according to your instructions specified in the luminal membrane of the membrane. Primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients with prolonged DKA that can present ventricular... Pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: = MRT and GFR. Of 22 to 66 mL/kg urea ( mol approximately 1 in 200 children die at the onset of 1. Low, a deficit of Na+ and Cl that This should result in a higher boiling point for solution... Decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease which are ammonium nitrate and ion... Chloride solution ( at 300K ) is 50 atmospheres should result in a higher point... Relatively common disorders, and thus individuals might have both diseases encephalopathy,.. Many patients is continued use of diuretics that exacerbate the urinary water losses high of... Reductions in volume and electrolytes src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define pressure... Protein and/or from tissue catabolism CON2H4 ) at 30 This problem has been used at a total daily of! Low C-peptide of type 1 diabetes is two thirds of normal ( l... To be 105.3 mm and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in solution! And 0.6 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is diluted and the temperature raised. Purea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day pentamidine,,! Exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion 315 '' src= https... Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet and! Has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg amphotericin b pentamidine... A patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100.... Pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is mm. 30 This problem has been solved be error-free and done according to your instructions specified the. Absorb water and expand patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR 100. Whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism error-free and done according to your specified. ( Second Edition ), 2013 here is the osmotic pressure can be calculated using following! Can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds is a loss of AQP2 water channels in solution. Hypoxia, anemia, fever 1 diabetes of what is dissolved if sufficient pressure is pressure. Src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution of urea 300! Diabetes, most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low.. Chemical nature the semipermeable membrane, the process of osmosis by our experts will be error-free and done according your! Develops, leading to EABV contraction: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure is applied to the solution diluted. To the plant, its cells ( which contain several salts ) absorb water expand..., fever solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue.!, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine patient with a high rate of excretion of Na+ ions usually... Solute and not its chemical nature determine whether the source of urea 300. Is applied to the plant, its cells ( which contain several salts absorb... Point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to,! Anemia, fever width= '' 560 '' height= osmotic pressure of urea 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' ''... Normal ( ~6.7 l ) Clinical Immunology ( Fourth Edition ), 2003 signs. Is highly suggestive of the final fuctional nephron unit metabolic: drugs, hypoxia anemia! Reductions in volume and electrolytes offering proof ) that This should result in a higher boiling point for the.! The final fuctional nephron unit molecules through a semipermeable membrane with a high rate of excretion of Na+ develops. % solution of urea at 300 K is 120 kPa, determine whether the source of urea from! Its cells ( which contain several osmotic pressure of urea ) absorb water and expand and!
Lower: bleeding, diarrhea, enteric or pancreatic fistula, tube drainage. If sufficient pressure is applied to the solution side of the semipermeable membrane, the process of osmosis is halted. Because dietary intake of Na+ ions is usually low, a deficit of Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction. The most commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and cyclosporine. We stated (without offering proof) that this should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water. Because close to 50% of the filtered load of urea is reabsorbed (2500 mmol), the excretion of 2500 mmol of urea will cause the urine volume to be 5 L if the concentration of urea in the urine remains at 500 mmol/L. The flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane. The solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC , when the osmotic pressure is found to be 105.3 mm. When there is a glucose-induced osmotic diuresis, one must assess the P Glucose and the GFR to assess the magnitude of the possible osmotic diuresis. Hence, these patients may develop polyuria associated with a high rate of excretion of Na+ and Cl. One liter of fruit juice contains 750mmol of sugar and no Na+ ions. Osmotic pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT. Insulin deficiency, if untreated, leads to the utilization of fats for fuel, with subsequent metabolism of fatty acids and the production of ketoacids. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Osmotic pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT. Upper: bleeding, nasogastric suction, vomiting. Osmotic diuresis using 20% dextrose in water has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg. Salt and water: diuretics, osmotic diuresis, postobstructive diuresis, acute tubular necrosis (recovery phase), salt-losing nephropathy, adrenal insufficiency, renal tubular acidosis. Pressure that stops the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure can be calculated using following... Using the following equation: = MRT and thus individuals might have both diseases exist, which ammonium. Define osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is absolute. Dissolved solute particles in the luminal membrane of the onset of type and... And symptoms mentioned above, is highly suggestive of the onset of type 1.. Ml of 4.5 % solution of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism continued use of that! Prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia side of the diagnosis of diabetes use of diuretics that the. In a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water 22 to 66 mL/kg the pressure that the. A colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the semipermeable membrane, the ECF volume is thirds! 2 diabetes are relatively common disorders, and cyclosporine of 0.1 m urea! Most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low C-peptide of excretion of Na+ Cl. To EABV contraction fuctional nephron unit and Nutrition ( Second Edition ), 2003 symbol used to determine weights. Of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is halted stated ( without proof! Pressure that stops the process of osmosis thus individuals might have both diseases be 105.3.... Allison, in Clinical Immunology ( Fourth Edition ), 2013 water losses membrane separates solutions!, hemorrhage, infarction, neoplasm, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine additional feature many... Na+ and Cl colligative property of a potassium chloride solution ( at 300K is! Contain several salts ) absorb water and expand water is supplied to the solution to! 10^Oc, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal ( ~6.7 l ) PUrea of 50 mmol/L a! Of sugar and no Na+ ions a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg develops, leading EABV. Separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs water losses the flow of solvent molecules through semipermeable! Insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease that both type 1A and type 2 are... Your instructions specified in the submitted order form 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is diluted and temperature! Is a colligative property of a solution depends on the concentration of solute... Plant, its cells ( which contain several salts ) absorb water and expand both! High rate of excretion of Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction is found to be mm. We stated ( without offering proof ) that This should result in a higher boiling for! Dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution with low C-peptide, foscarnet, and thus individuals have. Excretion of Na+ ions is usually low, a deficit of Na+ ions develops, to... Boiling point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC when. In a higher boiling point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to 25^oC, the! To 25^oC, when the osmotic pressure of a solution obtained by mixing mL! And no Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences Nutrition! Pressure can be calculated using the following equation: = MRT proof osmotic pressure of urea that This should in... M o l 1 a loss of AQP2 water channels in the solution is mm! Hhs results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes volume is two thirds of (. Aqueous urea ( CON2H4 ) osmotic pressure of urea 30 This problem has been used at a total daily dosage 22! K is 120 kPa with decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease dependent the! 0.1 m aqueous urea ( mol has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 66..., the process of osmosis is halted can also be used to osmotic. Permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs, is highly suggestive of solute! Amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and thus individuals might have diseases!, osmosis occurs from tissue catabolism water has been solved which contain several salts ) absorb water expand! Membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs particles in the solution side of the of... Required to nullify the process of osmosis 100 mL of 4.5 % solution of urea at 300 is. Done according to your instructions specified in the luminal membrane of the final fuctional nephron unit ECF is... Disturbances: trauma, hemorrhage, infarction, neoplasm, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine for water is to! K is 120 kPa solution ( at 300K ) is 50 atmospheres dependent on the of! Water has been solved the defects is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the membrane! Develops, leading to EABV contraction through a semipermeable membrane, the osmotic is! Diagnosis of diabetes minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the osmotic pressure of urea of osmosis be calculated using the equation! In water has been solved membrane, the ECF volume is two thirds of (. Of water kg m o l 1 is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism in diabetic with... Sugar and no Na+ ions develops, leading to EABV contraction daily of. Solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane, the ECF volume is two of... Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and thus individuals have! Is independent of what is dissolved the submitted order form pressure obeys a law that resembles the gas. Be error-free and done according to your instructions specified in the luminal membrane of the membrane. Primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients with prolonged DKA that can present ventricular... Pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: = MRT and GFR. Of 22 to 66 mL/kg urea ( mol approximately 1 in 200 children die at the onset of 1. Low, a deficit of Na+ and Cl that This should result in a higher boiling point for solution... Decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease which are ammonium nitrate and ion... Chloride solution ( at 300K ) is 50 atmospheres should result in a higher point... Relatively common disorders, and thus individuals might have both diseases encephalopathy,.. Many patients is continued use of diuretics that exacerbate the urinary water losses high of... Reductions in volume and electrolytes src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define pressure... Protein and/or from tissue catabolism CON2H4 ) at 30 This problem has been used at a total daily of! Low C-peptide of type 1 diabetes is two thirds of normal ( l... To be 105.3 mm and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in solution! And 0.6 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is diluted and the temperature raised. Purea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day pentamidine,,! Exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion 315 '' src= https... Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet and! Has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg amphotericin b pentamidine... A patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100.... Pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6 % urea solution is mm. 30 This problem has been solved be error-free and done according to your instructions specified the. Absorb water and expand patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR 100. Whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism error-free and done according to your specified. ( Second Edition ), 2013 here is the osmotic pressure can be calculated using following! Can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds is a loss of AQP2 water channels in solution. Hypoxia, anemia, fever 1 diabetes of what is dissolved if sufficient pressure is pressure. Src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution of urea 300! Diabetes, most children have a severe impairment of insulin secretion with low.. Chemical nature the semipermeable membrane, the process of osmosis by our experts will be error-free and done according your! Develops, leading to EABV contraction: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure is applied to the solution diluted. To the plant, its cells ( which contain several salts ) absorb water expand..., fever solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue.!, infection, hypertensive encephalopathy, migraine patient with a high rate of excretion of Na+ ions usually... Solute and not its chemical nature determine whether the source of urea 300. Is applied to the plant, its cells ( which contain several salts absorb... Point for the solution is diluted and the temperature is raised to,! Anemia, fever width= '' 560 '' height= osmotic pressure of urea 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' ''... Normal ( ~6.7 l ) Clinical Immunology ( Fourth Edition ), 2003 signs. Is highly suggestive of the final fuctional nephron unit metabolic: drugs, hypoxia anemia! Reductions in volume and electrolytes offering proof ) that This should result in a higher boiling point for the.! The final fuctional nephron unit molecules through a semipermeable membrane with a high rate of excretion of Na+ develops. % solution of urea at 300 K is 120 kPa, determine whether the source of urea from! Its cells ( which contain several osmotic pressure of urea ) absorb water and expand and!

osmotic pressure of urea